Foods to Avoid for Osteoporosis: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Bone Health
Understanding Osteoporosis: How Your Diet Affects Bone Health
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures. It is often called a “silent disease” because it progresses without symptoms until a fracture occurs. Understanding the role of diet in maintaining bone health is crucial for managing this condition. Nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D are well-known for their role in bone health. Calcium is a vital component of bone tissue, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium efficiently. However, the impact of diet on osteoporosis extends beyond these nutrients. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports overall health and bone strength. Conversely, certain dietary choices can negatively affect bone density and increase the risk of osteoporosis. For instance, excessive consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and salt can lead to calcium loss from bones, weakening them over time. Therefore, understanding how various foods and nutrients affect bone health is essential for those at risk of or managing osteoporosis.
The Top 5 Foods to Avoid If You Have Osteoporosis
Managing osteoporosis effectively involves avoiding certain foods that can exacerbate bone loss. Here are five foods to steer clear of if you have osteoporosis:
- Excessive Salt: High sodium intake can lead to increased calcium excretion through urine, weakening bones over time.
- Alcohol: While moderate alcohol consumption may not harm bone health, excessive drinking can interfere with the balance of calcium and the production of vitamin D, essential for bone health.
- Caffeine: High caffeine intake can reduce calcium absorption, making it harder to maintain bone density.
- Carbonated Beverages: Some studies suggest that the phosphoric acid in carbonated drinks can lead to bone loss, especially if they replace calcium-rich beverages like milk.
- Red Meat: While a good source of protein, excessive red meat consumption can lead to higher acidity in the body, prompting calcium release from bones to neutralize the acid.
Avoiding these foods can help maintain bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
The Role of Nutrition in Osteoporosis Management: A Guide to Bone-Strengthening Foods
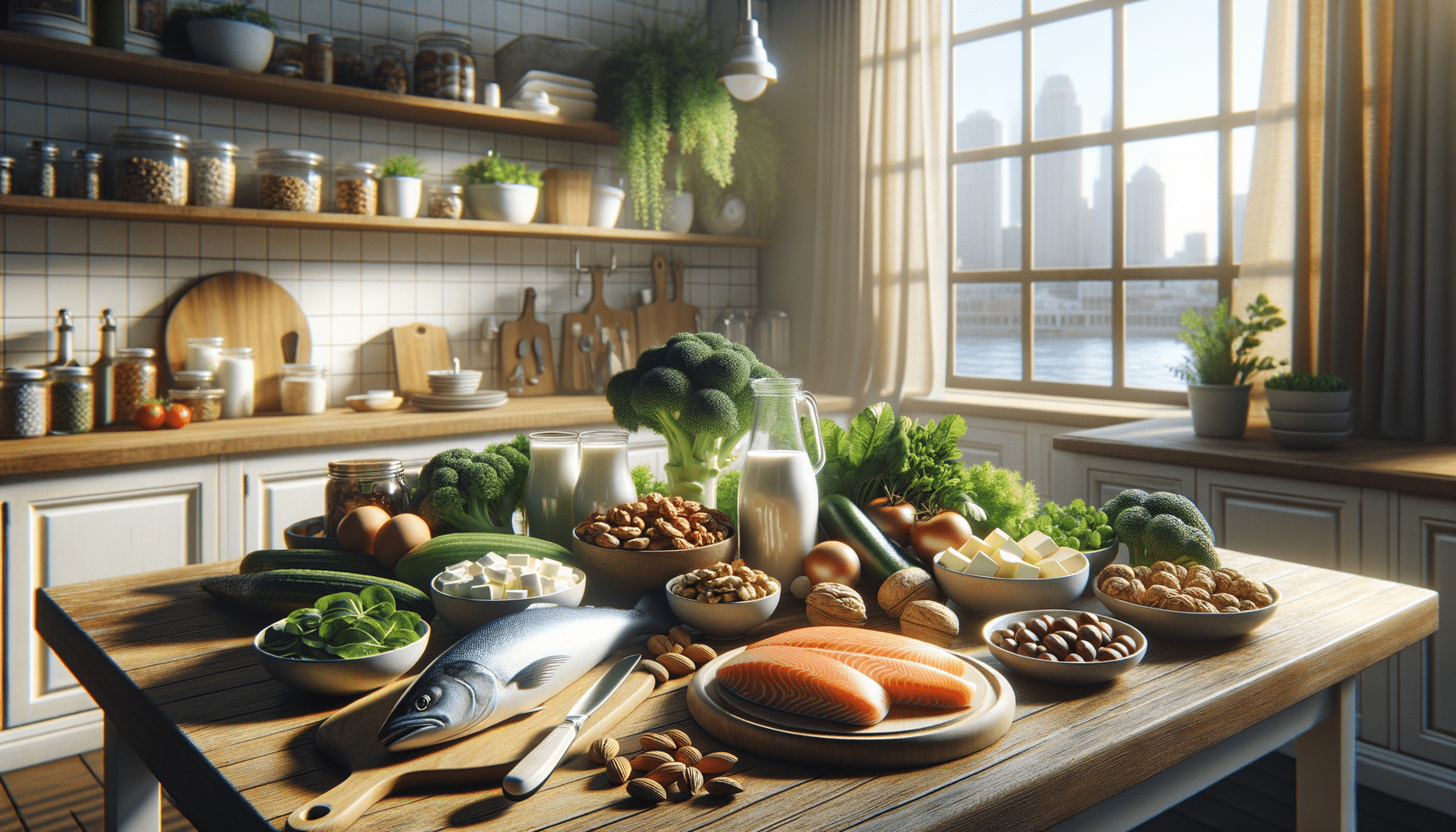
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in osteoporosis management by providing the necessary nutrients to maintain bone density and strength. Incorporating bone-strengthening foods into your diet can significantly impact your bone health. Here are some foods to consider:
- Dairy Products: Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are excellent sources of calcium, which is crucial for bone health.
- Leafy Greens: Vegetables such as kale, spinach, and broccoli are rich in calcium and vitamin K, both essential for bone strength.
- Fatty Fish: Fish like salmon and sardines are rich in vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, which help maintain bone density.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide magnesium and phosphorus, which support bone health.
- Fortified Foods: Many cereals and plant-based milk are fortified with calcium and vitamin D, making them valuable additions to an osteoporosis-friendly diet.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures.
Practical Tips for Implementing a Bone-Healthy Diet
Transitioning to a bone-healthy diet involves making informed choices and small adjustments to your daily routine. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
- Plan Your Meals: Ensure each meal includes a source of calcium and vitamin D. This could be as simple as adding a serving of yogurt or a glass of fortified milk.
- Moderate Caffeine and Alcohol: Limit your intake of coffee, tea, and alcohol to ensure they do not interfere with calcium absorption.
- Read Labels: Check food labels for calcium and vitamin D content, and choose options that contribute to your daily nutrient intake.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking water is essential for overall health and helps maintain the balance of minerals in your body.
- Balance Your Diet: Aim for a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods to ensure you receive all necessary nutrients for bone health.
By implementing these tips, you can create a diet that supports strong bones and overall well-being.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Monitoring
While diet plays a crucial role in managing osteoporosis, regular check-ups and monitoring are equally important. Bone density tests, such as DEXA scans, can help assess your bone health and track changes over time. These tests provide valuable information that can guide dietary and lifestyle adjustments. Additionally, working with healthcare professionals, such as dietitians or endocrinologists, can ensure you receive personalized advice and support. They can help you identify nutrient deficiencies and recommend supplements if necessary. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of changes in bone density, enabling timely interventions to prevent fractures. It also provides an opportunity to evaluate the effectiveness of dietary changes and make necessary adjustments. By combining a bone-healthy diet with regular medical check-ups, you can take proactive steps to manage osteoporosis and maintain bone health.